Basic guideline of intellectual property rights
Read in Indonesian
Indonesian citizens are not the only ones who often got caught in problems related to authorisation and use of artists or designers' creation. Government institutions do too. Recently, an electronic company was using a song by a Norwegian singer without permission for its mobile phone advertisement.
Artwork comes in various forms, and its protection depends on the categories in the intellectual property rights (HKI). According to the World Intellectual Property Organisation, intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions, artistic works, symbols, names, drawings and images used in commerce.
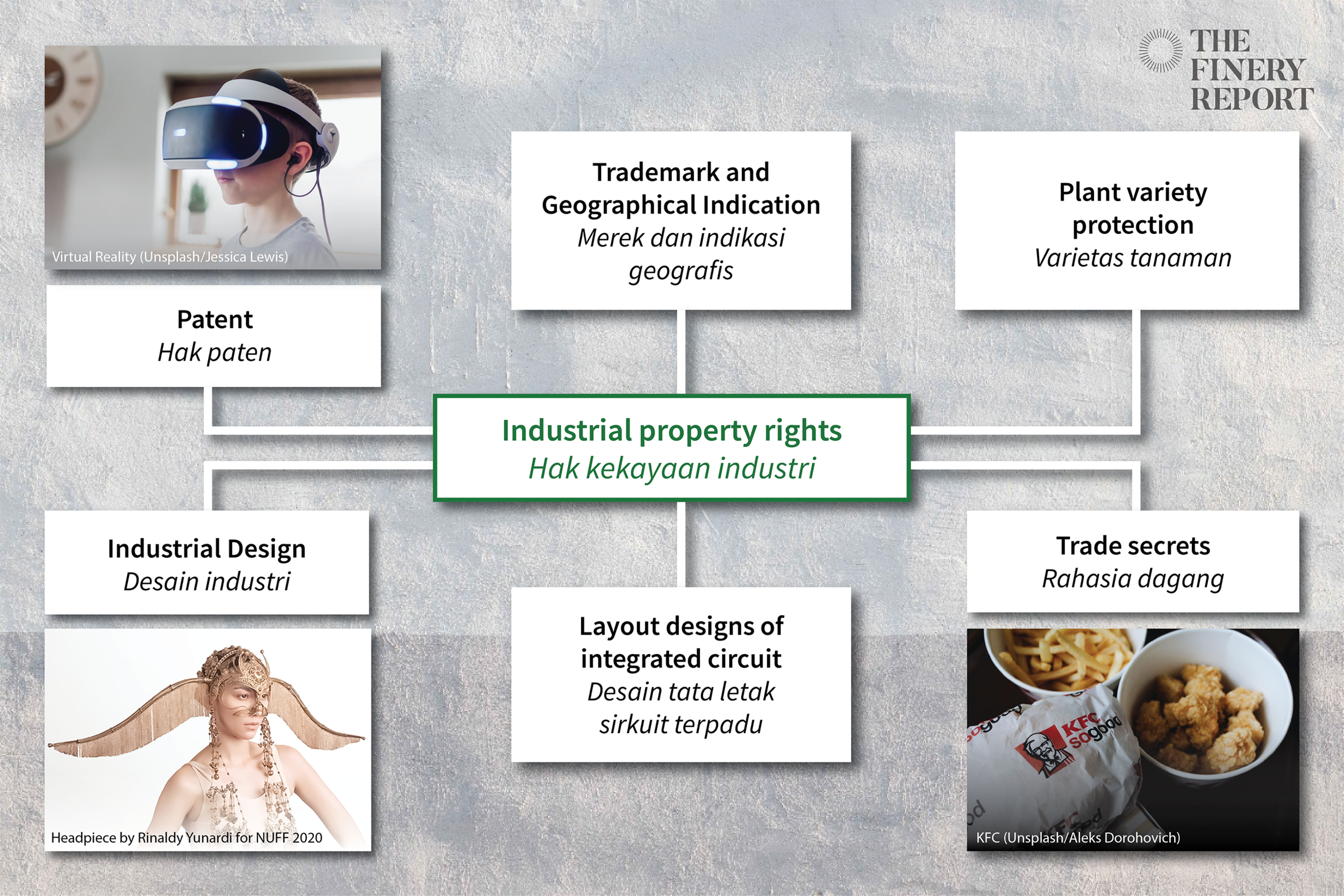
There are seven types of IP rights which are divided into two categories: copyright and industrial property rights. Industrial property rights include trademark and geographical indication, industrial design, patent, layout designs of integrated circuit, plant variety protection and trade secret.
Copyright protects artwork while industrial property rights protect assets with economic value in commercial activity.
The Existence of Personality theory by Frederich Hegel stated that IP rights as intellectual work is the embodiment of an individual’s existence, therefore should not only be rewarded economically, but also morally.
This is what underlines the regulation of intellectual property rights in Indonesia. Therefore, we as citizens are expected to play a part in giving proper respect to creators, not only economically, but also morally.
The following is the summary of each intellectual property rights’ category
Copyright (Law No.28 Year 2014 about Copyright)
Exclusive rights for creators or copyright owners that automatically appear upon completing an artwork. Copyright protection is granted to original artwork that has been completed. Ideas cannot be protected.
A copyright lasts for the creator's lifetime plus 70 years after the creator passes away. Corporation receives 50 years of protection after registration.
Industrial property rights include:
1. Trademark and geographical indication right (Law No.20 Year 2016 about Trademark and Geographical Indication)
Exclusive rights granted to owner of registered trademark for personal use. Trademark owners are allowed to grant permission to others to use their mark.
Trademark consists of picture, logo, name, word, letter, number and colour combination. Trademark can be in 2D, 3D, hologram and sound format. A trademark is eligible for registration when it is different from other registered trademarks and popular trademarks.
Trademark protection is valid for 10 years. Owner can extend the protection.
2. Industrial design (Law No.31 Tahun 2000 about Industrial Design)
Industrial design protects shapes along with line and colour combination of a product. Basic shapes like square, circle and triangle cannot be registered. Design has to be original and can be reproduced.
Industrial design protection lasts for 10 years after the date of registration.
3. Patent right (Law No.13 Year 2016 about Patent Rights)
Patents protect ideas and inventions in technology beneficial for human lives. An invention that affects survival, such as vaccine, cannot obtain patent protection.
Patent protection is valid for 20 years and 10 years for a simple patent. Patent protection cannot be extended. Simple patent is a development of existing product or process that has been implemented in the industry. The development has to be more practical than the previous invention in short amount of time with simple method and relatively affordable cost.
4. Layout designs of ntegrated circuit (Law No.32 Year 2000 about Layout Designs of Integrated Circuit)
The law protects both finished and semi-finished electronic circuit design in 3D shape and partly or entirely are interconnected and integrated forming in a semiconductor. The protection is granted since the first commercial exploitation of the design at any place, or from the filing date.
The protection is valid for 10 years and cannot be extended.
5. Plant variety (Law No.29 Year 2000 about Plant Variety Protection)
Plant variety protection is granted to new type of plants produced using the plant breeding method. Plant breeding is a genetic engineering method to produce desired characteristics.
The protection is valid for 25 years for perennial plants like trees and 20 years for annual or biennial plants.
6. Trade secret (Law No.30 Year 2000 about Trade Secret)
Trade secret is an information kept secret from the public due to its economic value in business. Trade secrets include customer list, market research, technical research, food recipes or ingredients, financial information, or price list with margin.
Trade secret protection lasts forever.